You can find four main types of gas cylinders. These are Type 1 (all-metal), Type 2 (hoop-wrapped), Type 3 (fully-wrapped with metal liner), and Type 4 (composite gas cylinder). Each type is made in a different way. Each type has special features. Each type is used for different things. People use gas cylinders in many areas. They are used in the chemical industry to store gases. They are used in food and drinks to keep things fresh. Here is a quick look at where you might see each type:
Type of Gas Cylinder | Common Applications |
Type 1 | Storing and moving liquefied gases (butane, propane, refrigerants) |
Type 2 | Storing and moving compressed gases (compressed air, nitrogen, oxygen) |
Type 3 | Storing and moving compressed gases (hydrogen, natural gas) |
Type 4 | Storing and moving compressed gases (hydrogen) |
Key Takeaways
There are four main types of gas cylinders. These are Type 1 (all-metal), Type 2 (hoop-wrapped), Type 3 (fully-wrapped metal liner), and Type 4 (composite). Each type has special features and uses.
Type 1 cylinders are strong and last a long time. They work well for high-pressure jobs. But they are heavy. They need regular checks to stop rust.
Type 2 cylinders weigh less than Type 1. They cost less too. But their fiber wrap needs to be checked often.
Type 3 cylinders are not too heavy and are strong. They are good for high-pressure gases. But they cost more money. They must be handled with care.
Type 4 cylinders are the lightest and easiest to carry. They are best when weight matters most. But they cost more.
Type 1: All-Metal Cylinder
Construction
Type 1 cylinders are made only from metal. Most are made from steel or aluminum. Steel is strong and lasts a long time. Aluminum is lighter and does not rust easily. Both can be shaped into one solid piece. This means there are no welded parts. This helps the cylinder last longer and stay safe. Special machines shape the metal with heat and spinning. This makes the size and shape very exact. You can see what each material is used for in the table below:
Material | Description | Use Cases |
Steel | Durable, lower cost, but heavier | Industrial gas, medical oxygen/air |
Aluminum | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, more portable | Medical oxygen, SCUBA, specialty gas |
Seamless Steel | One-piece, long service life | Industrial gas, medical oxygen/air |
Seamless Aluminum | Corrosion-resistant, seamless shell | Medical oxygen, SCUBA, specialty gas |
Features
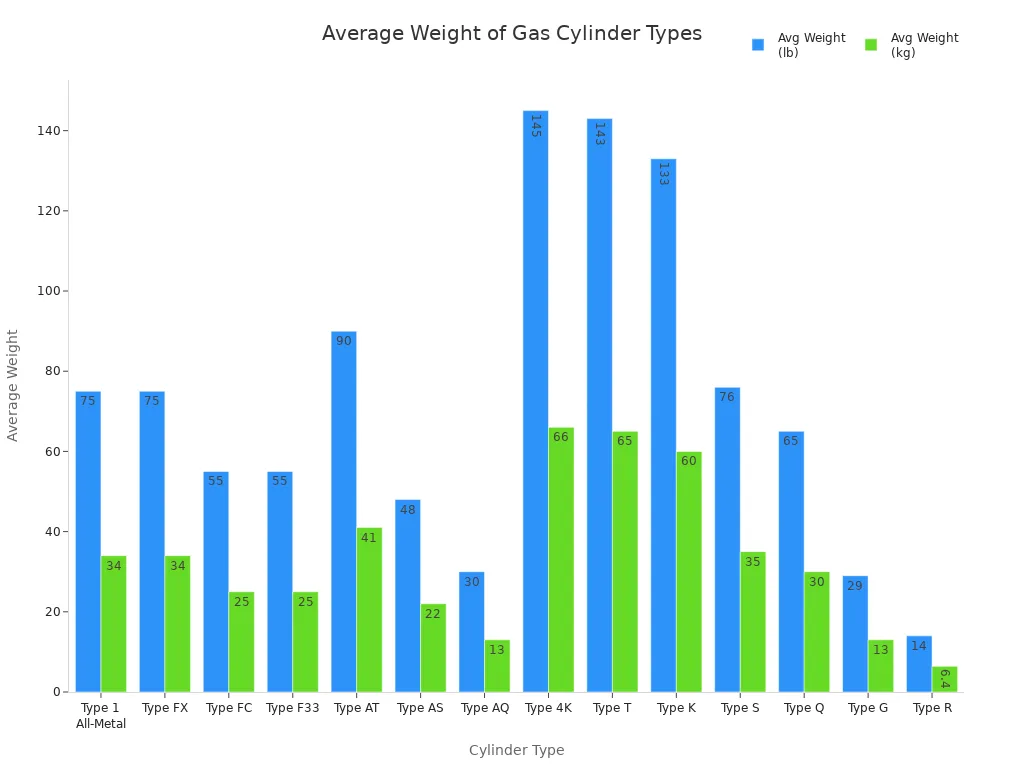
Type 1 all-metal cylinders are simple and strong. They can hold many kinds of gases. These include compressed air, oxygen, and specialty gases. They can handle high pressure and work in tough places. Most Type 1 cylinders are heavier than other types. The average weight is about 75 pounds (34 kg). You can see how much different cylinders weigh in the chart below:
Pros
There are many good things about Type 1 all-metal cylinders. They are very strong and can hold high pressure. Each one is tested to make sure it is safe. They do not leak gas. You can use them in many countries because they follow safety rules. The table below shows the main good points:
Advantage | Description |
High-strength steel | Withstands high pressures and reduces risk of failure |
Precise manufacturing | Undergoes strict testing for top performance |
Leak-proof design | Keeps gas safely contained under extreme conditions |
Global approvals | Meets international safety standards |
Maximum Safety | Built for extreme conditions |
Extended Service Life | Lasts a long time with proper care |
Efficiency | Needs little maintenance and works in many situations |
Cons
There are some problems with Type 1 all-metal cylinders:
These cylinders are heavy and hard to move.
Steel cylinders can rust, so you must check them often.
They are not great for carrying around because of their weight.
You need to inspect them often to stop rust.
Tip: If you want a cylinder you can carry, try a lighter one.
Type 2: Hoop-Wrapped Cylinder
Construction
Type 2 hoop-wrapped cylinders use more than one material. The main part is a forged steel liner. This liner makes the cylinder strong and tough. Carbon fiber is wrapped around the middle part. This wrap makes the cylinder lighter but still safe. The top and bottom are not wrapped. The table below lists the materials used:
Material Type | Description |
Forged Steel Liner | Provides strength and durability |
Carbon Fiber Overwrap | Reduces weight while maintaining safety and performance |
This design gives you a cylinder that is strong and not too heavy. The fiber, soaked in resin, is often fiberglass or carbon. It makes the middle part even stronger. This way, the cylinder is safe and not too heavy.
Features
Type 2 cylinders are special because of their hoop-wrapped design. They are lighter than Type 1 but heavier than Type 3. The inside liner is made of aluminum and holds high pressure. The middle part uses carbon fiber or fiberglass for more strength. You can use these cylinders for hydrogen, CNG, and medical breathing gases. Here are some features:
Made with aluminum and a carbon fiber wrap
Good for hydrogen, CNG, and medical breathing gases
Can hold a lot of gas for storage
Middle part is stronger for safety
Pros
Type 2 hoop-wrapped cylinders have many good points. They are lighter than all-metal cylinders, so they are easier to move. You can store more gas because they hold a lot. They cost less than Type 1 cylinders. For example, one Type II-S cylinder can cost about half as much as four Type I cylinders. If you need more storage, you save money on things like pipes and valves. The hoop-wrapped design helps the cylinder handle high pressure.
Note: Type 2 cylinders help you save money and keep your storage safe.
Cons
There are some things to think about. Type 2 cylinders are heavier than fully composite cylinders. The top and bottom, which are not wrapped, may not be as strong. You need to check the fiber wrap often for damage. These cylinders are not the best if you want the lightest one.
Heavier than Type 3 and Type 4 cylinders
Top and bottom may not be as strong
Need to check the fiber wrap often
Type 3: Fully-Wrapped Metal Liner
Construction
A Type 3 fully-wrapped metal liner cylinder uses both metal and composite materials. The inside liner is made from aluminum. This liner gives the cylinder its shape and keeps the gas inside. High-strength composite materials, like carbon fibers, wrap around the whole liner. The wrap covers the entire cylinder, not just the middle part. These materials together make the composite gas cylinder strong and light.
Material Type | Description |
Metal Liner | Typically made of aluminum |
Composite Materials | High-strength composite materials such as carbon fibers |
Features
A Type 3 composite gas cylinder is light and can hold high pressure. You can carry it easier than a steel cylinder. It does not rust or get damaged by weather. This cylinder holds a lot of gas at high pressure. For example, a Type 3 cylinder can hold 18.0 liters of gas. It weighs about 11.0 kg. It can handle a working pressure of 300 bar. The test pressure can go up to 450 bar. This makes it good for storing gases like argon, helium, and medical-grade gases.
Feature | Details |
Capacity | 18.0 liters |
Weight | 11.0 kg |
Working Pressure | 300 bar |
Test Pressure | 450 bar |
You will see this composite gas cylinder in aerospace, electronics, and medical fields. People also use it for high-altitude ballooning and other places where weight is important.
Pros
There are many good things about a Type 3 composite gas cylinder:
It is easy to move because it is light.
The cylinder can store more gas at higher pressures.
It is strong and safe for holding compressed gases.
You do not have to worry much about rust.
The cylinder lasts a long time, even in tough places.
Advantage | Benefit |
Lightweight | Increased mobility and reduced fatigue for users. |
High Pressure Capability | Ability to store more gas at higher pressures, enhancing usability. |
Strength | Exceptional strength allows for safe storage of compressed gases. |
Durability | Resistant to impacts and wear, ensuring longevity. |
Corrosion Resistance | More resilient in harsh environments, preventing degradation over time. |
Tip: Carbon fiber in the composite gas cylinder makes it strong but not heavy. This means you get safety and easy handling at the same time.
Cons
There are some things to think about. A Type 3 composite gas cylinder costs more than a Type 1 or Type 2 cylinder. You need to check the cylinder for damage to the composite wrap. If you use it in rough places, you must inspect it often. The aluminum liner can dent if you drop the cylinder. It is not as light as a Type 4 composite gas cylinder.
Costs more than metal-only cylinders
Needs regular checks for wrap damage
Aluminum liner can dent if dropped
Not as light as a Type 4 composite gas cylinder
Type 4: Composite Gas Cylinder
Construction
Type 4 composite gas cylinders use special materials. The inside liner is a strong polymer, not metal. This liner keeps the gas inside and stops leaks. The outside shell is made from carbon fiber and epoxy resin. The carbon fiber wraps all the way around the cylinder. This makes the cylinder keep its shape and stay strong.
Component | Material Description |
Polymer Liner | Non-metallic, high-strength polymer |
Carbon Composite Shell | Fully wrapped with carbon fiber and epoxy resin |
This mix of materials makes the cylinder light and tough. The polymer liner does not rust. The carbon fiber shell makes it even stronger.
Features
Type 4 cylinders are very light and strong for their weight. You can carry them without much trouble. The carbon fiber wrap lets them hold high-pressure gases. People use these cylinders in cars, trucks, and airplanes. They are good when you need to save weight.
Some special features are:
Light design makes them easy to move and use.
Carbon fiber wrap helps them hold high pressure.
The high-polymer coat protects from weather and chemicals.
Rubber caps and layers help protect from bumps.
Flame-retardant design keeps them safe in heat.
Tip: If you need a cylinder for moving or high-tech jobs, Type 4 is a smart pick.
Pros
Type 4 composite gas cylinders have many good points:
They weigh about one-third as much as steel cylinders. You can move them easily.
The polymer and carbon fiber do not rust. This means they last longer, even in wet or salty places.
The high strength-to-weight ratio lets you store more gas without making the cylinder heavy.
You can use them in cars, buses, and planes where weight matters.
Advantage | Description |
Portability | Easy to carry and install |
Corrosion Resistance | No rust, longer life |
High Pressure | Safe for high-pressure gases |
Versatility | Used in many industries |
Cons
There are some things you should know:
Type 4 cylinders cost more than metal ones. The special materials and design make them more expensive.
They do not last as long. You may need to get new ones more often than steel cylinders.
It is hard to know if they have long-term damage. You must check them often, especially for important uses.
Disadvantage | Type 4 Composite Gas Cylinders | Metal Gas Cylinders |
Cost | Higher price tag | Lower cost |
Long-term Durability | Limited lifespan, frequent replacement | Longer lifespan, less frequent replacement |
Note: If you want the lightest and easiest cylinder to carry, Type 4 is best. If you want a cylinder that lasts many years, you might want a metal one.
There are big differences between the four gas cylinder types. Type 1 is made from all metal. It is the heaviest one. But it lasts the longest. Type 2 and Type 3 have metal liners with fiber wraps. This makes them lighter but still strong. Type 4 is a composite gas cylinder. It has a plastic liner and carbon fiber wrap. This makes it the lightest choice. Look at the table below to compare weight, how long they last, and cost:
Type | Material Composition | Weight | Durability | Cost Implications |
Type 1 | Entirely metal | Heaviest | Most durable | Higher due to material |
Type 2 | Metal liner reinforced with glass fiber | Moderate | Durable | Cost-effective |
Type 3 | Aluminum liner fully wrapped in carbon fiber | Light | Durable | Moderate |
Type 4 | Plastic liner fully wrapped in carbon fiber | Lightest | Durable | Most expensive |
If you want something easy to carry, choose a composite gas cylinder. If you do not want to spend much, steel or aluminum is a good pick. Use this table to help you decide:
Cylinder Type | Material | Portability | Cost |
Steel | Steel | Low | Low |
Aluminium | Aluminium | High | Medium |
Composite | Composite Wrap | High | High |
Tip: Think about where you will use the cylinder. Also, think about how often you need to move it. This will help you pick the best type for your needs.
FAQ
What is the safest type of gas cylinder?
You get the highest safety with Type 1 all-metal cylinders. These cylinders use strong steel or aluminum. They pass strict safety tests. You can trust them for tough jobs.
How do you know when to replace a gas cylinder?
Check for dents, rust, or leaks. If you see damage, replace the cylinder. Always follow the manufacturer's guidelines for service life.
Can you use composite cylinders for cooking gas?
You can use composite cylinders for cooking gas. They are light and easy to carry. Many people choose them for home and outdoor cooking.
Why do some cylinders cost more than others?
Cylinders with advanced materials like carbon fiber cost more. They are lighter and last longer in tough places. You pay for better performance and easier handling.